Overview
This article serves as a definitive guide to mastering file downloads with Curl, a powerful command-line utility for data transfer. It meticulously details the installation process across various operating systems, ensuring that users can easily set up Curl on their preferred platform.
Essential commands for downloading files are outlined, providing readers with the tools they need to execute their tasks efficiently. Additionally, the article offers troubleshooting tips for common issues, empowering users to navigate challenges with confidence.
By equipping readers with this vital knowledge, the article positions Curl as an indispensable asset for effective data management.
Introduction
Curl has emerged as an indispensable tool for developers and system administrators alike, enabling efficient data transfer across various protocols without the need for a graphical interface. This powerful command-line utility not only simplifies the process of downloading files but also enhances productivity by streamlining API interactions and automating data workflows.
However, many users may find themselves grappling with its myriad commands and potential pitfalls. How can one master the art of downloading files with Curl and avoid common errors that can disrupt their workflow?
Mastering Curl is not just about understanding commands; it’s about transforming the way you handle data. Dive into the world of Curl and unlock its full potential.
Understand Curl and Its Purpose
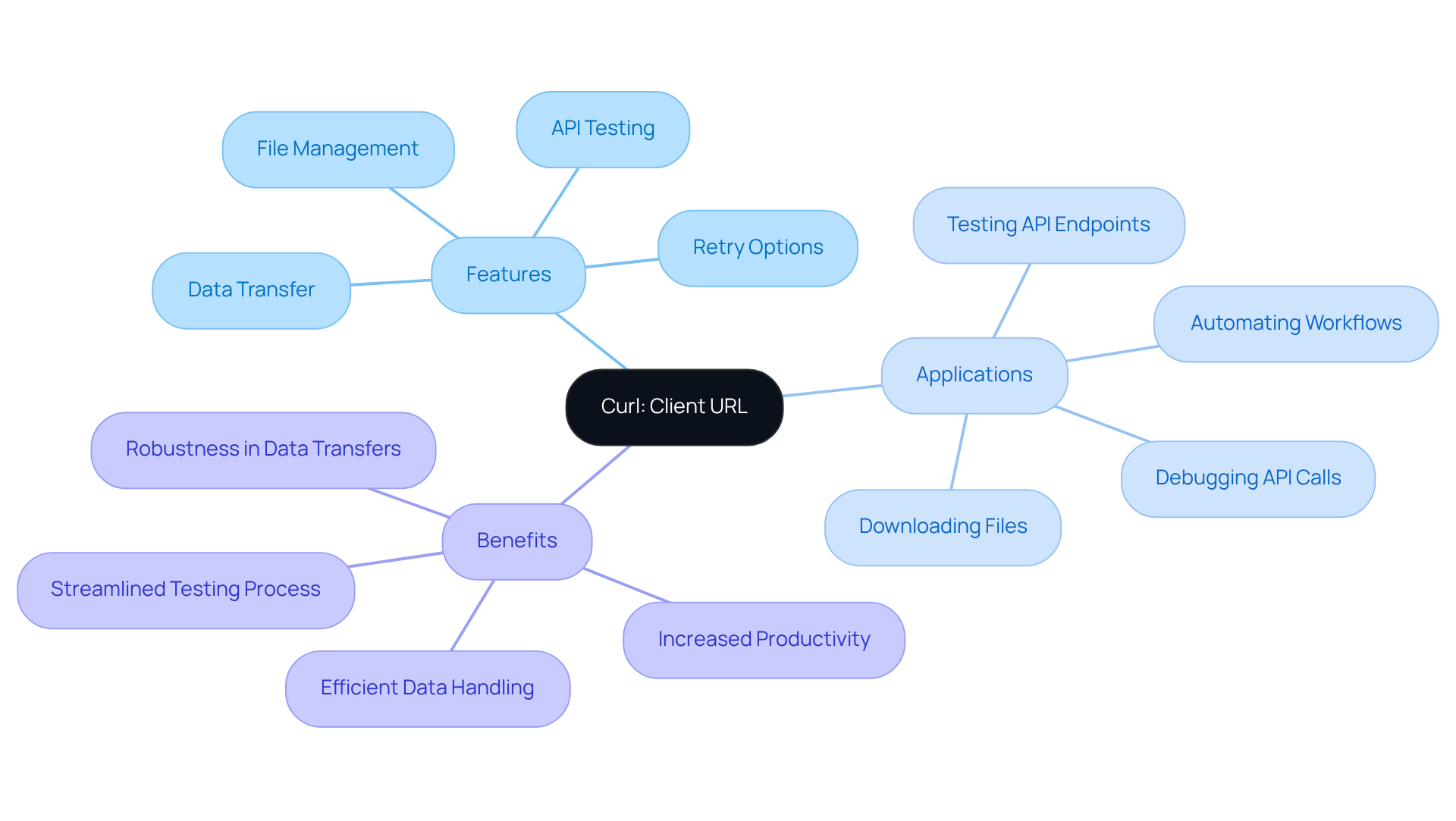
Curl', an acronym for 'Client URL', stands as a powerful command-line utility designed for seamless data transfer to and from servers using various protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. Its widespread adoption among developers is evident, with a significant percentage relying on command-line tools like Wget for tasks such as downloading documents, making API requests, and automating data transfers. This functionality empowers users to manage documents and , without the need for a web browser.
Developers frequently leverage command-line tools to test APIs, facilitating direct request and response interactions from the command line. This approach not only streamlines the testing process but also boosts productivity by enabling quick iterations and adjustments. Additionally, the ability to download files with curl, as well as manage uploads, positions Curl as an essential tool for automating data workflows and simplifying the handling of large datasets.
In practical applications, this tool can be used to download files with curl directly from specified URLs, preserving original titles or modifying them as needed. This feature proves particularly advantageous for sysadmins seeking efficient file management solutions. Furthermore, Curl supports the --retry option, allowing automatic attempts of failed requests, thereby enhancing its robustness in data transfer tasks. It also manages redirects seamlessly with the -L flag, ensuring uninterrupted data retrieval.
By grasping the purpose and capabilities of Curl, users can harness its powerful features to optimize data transfer processes and improve operational efficiency. For example, a typical command to save response data to a file is curl https://api.example.com/data --output response.json, illustrating how users can directly capture data from API responses.
Install and Configure Curl
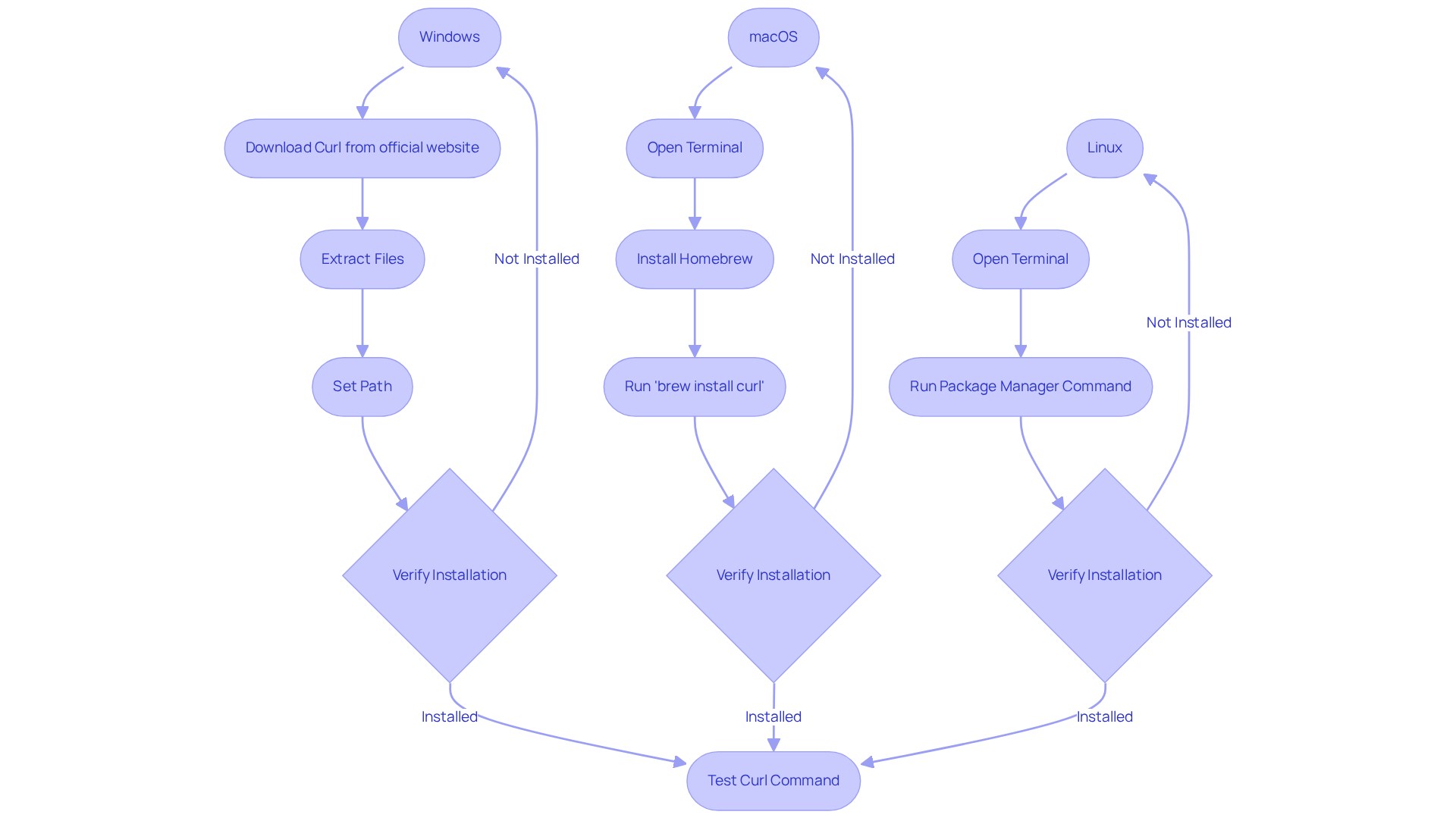
To install Curl, follow these steps based on your operating system:
For Windows:
- To download files with curl, you should visit the official Curl website and download the Windows version suitable for your system.
- Extract Files: Unzip the downloaded file and locate
curl.exewithin the extracted folder. - Set Path: Create a folder called 'curl' in your C: drive, move
curl.exeto this directory, and add this directory to your system's PATH environment variable to enable command-line access. Remember to replace any backslashes at the end of command lines with caret (^) characters to avoid issues with line continuation.
For macOS:
- Using Homebrew: Open the Terminal application and execute the command
brew install curl. You may need to after running this command. - Verify Installation: After installation, confirm that the tool is installed by typing
curl --versionin the terminal.
For Linux:
- Using Package Manager: Open the Terminal and run the appropriate command for your distribution:
- For Ubuntu:
sudo apt install curl - For CentOS:
sudo yum install curl
- For Ubuntu:
- Check Installation: Verify the installation by executing
curl --versionin the terminal.
After setup, ensure the tool is configured properly by verifying its version and executing a simple command such as [curl https://www.example.com](https://insights.exa.ai/10-benchmark-talent-datasets-for-vc-teams-to-enhance-performance) to download files with curl and test connectivity. Furthermore, you can verify your cURL installation by sending a request to the Zendesk API to obtain user information, utilizing a command such as curl https://subdomain.zendesk.com/api/v2/users/me.json -v -u email_address/token:api_token. This step is essential for confirming that the tool is operating as anticipated in your environment.
Execute the Download Command
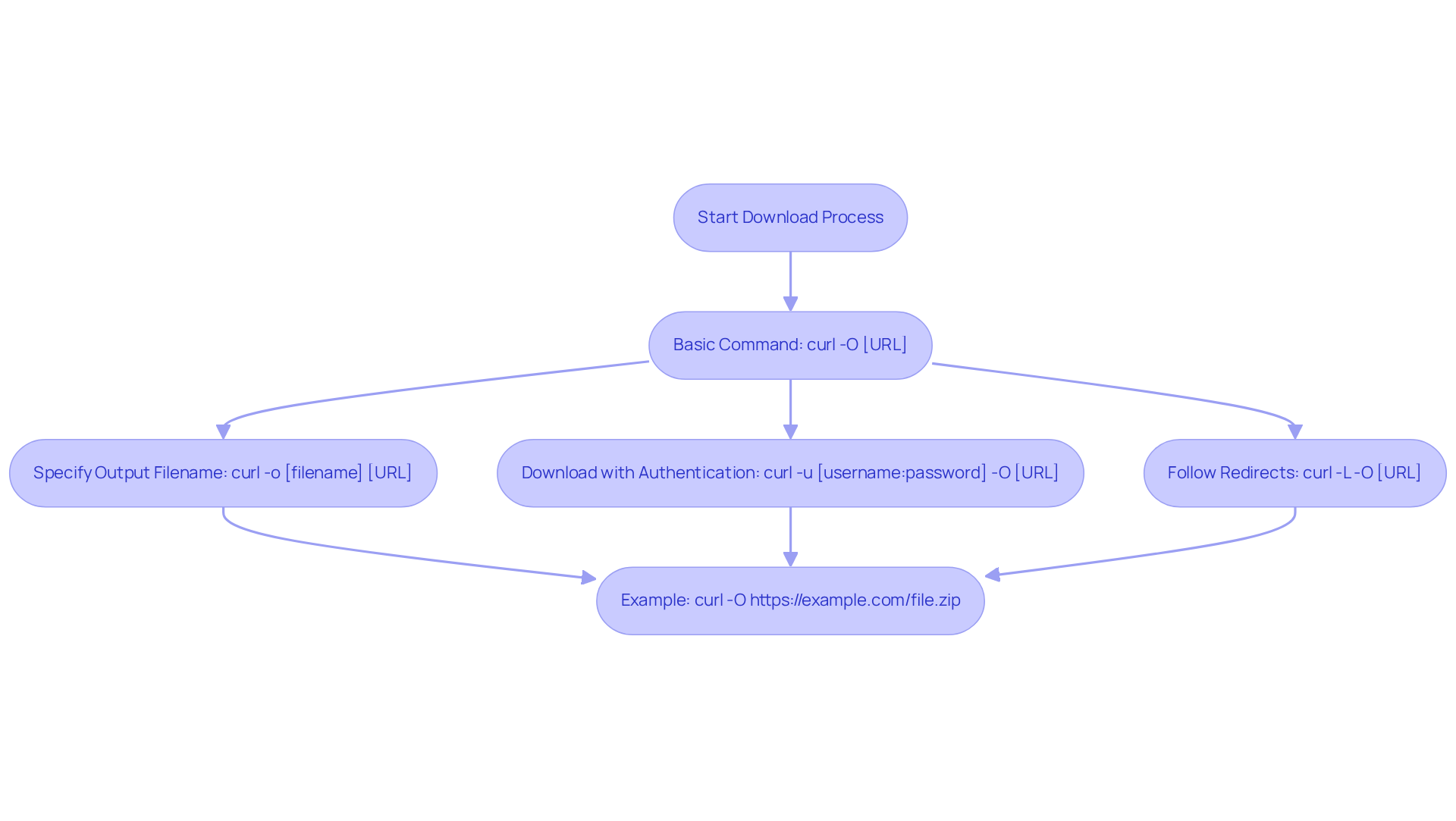
To effectively download a file using Curl, adhere to these essential steps:
-
Basic Command: Begin with the following syntax:
curl -O [URL]Here, replace
[URL]with the link to the file you wish to download. The-Ooption allows you to download files with curl, ensuring the document is saved with its original name, providing clarity and ease of access. -
Specify Output Filename: If you prefer a different name for the file, utilize this command:
curl -o [filename] [URL]Simply replace
[filename]with your desired file name, allowing for personalized organization of your downloads. -
Download with Authentication: In instances where authentication is required, the command adjusts as follows:
curl -u [username:password] -O [URL]Ensure you substitute
[username:password]with your actual credentials to facilitate a secure download. -
Follow Redirects: To guarantee Curl follows any redirects, incorporate the
-Loption:curl -L -O [URL]This ensures that even if the file location changes, your download proceeds uninterrupted.
-
Example: For practical application, consider this example: to download a file from
https://example.com/file.zip, execute:curl -O https://example.com/file.zipThis command will seamlessly download
file.zipinto your current directory, streamlining your workflow.
Troubleshoot Common Curl Issues
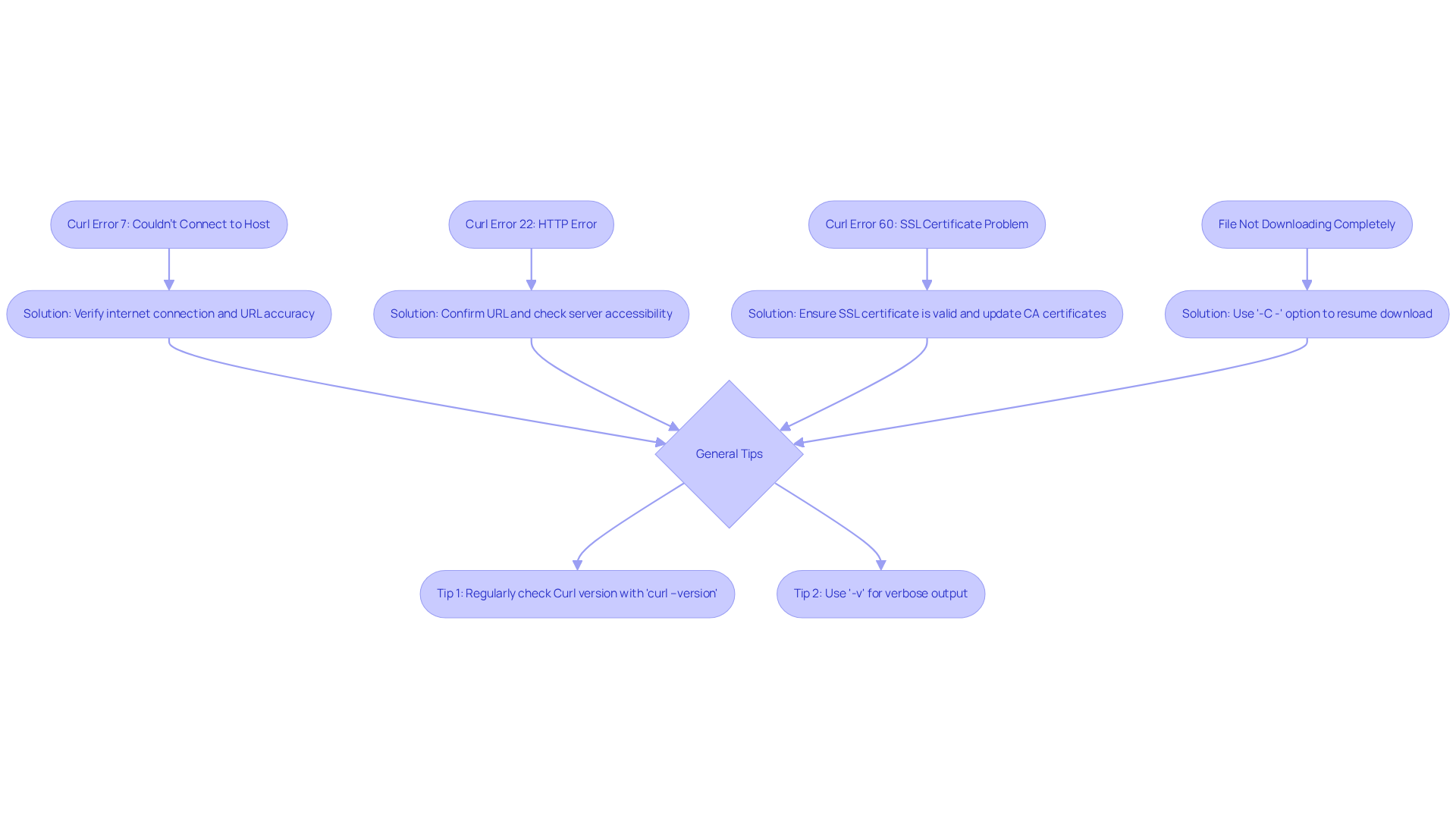
Common issues users may encounter with Curl and effective troubleshooting methods are outlined below:
-
Curl Error 7: Couldn't Connect to Host
Solution: Verify your internet connection and ensure the URL is accurate. Be aware that firewalls may obstruct requests made with Curl. -
Curl Error 22: HTTP Error
Solution: This error signifies a problem with the HTTP request. Confirm the URL and check the server's accessibility. -
Curl Error 60: SSL Certificate Problem
Solution: Ensure the server's SSL certificate is valid. Updating your CA certificates may be necessary. -
File Not Downloading Completely
Solution: If a file fails to download fully, utilize the-C -option to resume the download:curl -C - -O [URL] -
General Tips:
- Regularly check your Curl version with
curl --versionto confirm you are using the . - Employ the
-voption for verbose output, aiding in issue diagnosis:
curl -v [URL] - Regularly check your Curl version with
Conclusion
Mastering the art of downloading files with Curl equips users with a powerful tool for efficient data management and transfer. This guide illuminates the various functionalities of Curl, from installation across different operating systems to executing specific commands for seamless file downloads. Understanding Curl enhances productivity and streamlines workflows in various development and administrative tasks.
Key insights include:
- The installation process tailored for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Essential commands like
curl -Ofor straightforward downloads. - Methods for handling authentication and redirects.
- Troubleshooting common Curl errors to ensure users can swiftly resolve issues and maintain an uninterrupted workflow.
By leveraging Curl's robust features, users can optimize their data transfer processes and enhance operational efficiency.
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, mastering Curl transcends mere technical skill; it becomes a vital asset for developers, sysadmins, and anyone involved in data management. Embracing this tool can lead to significant improvements in productivity and data handling capabilities. Therefore, whether you are a seasoned developer or a newcomer, exploring the full potential of Curl unlocks new efficiencies and streamlines everyday tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Curl and what is its purpose?
Curl, which stands for 'Client URL', is a command-line utility designed for transferring data to and from servers using various protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
Why do developers use Curl?
Developers use Curl to manage documents, download files, make API requests, and automate data transfers efficiently without needing a web browser.
How does Curl benefit the API testing process?
Curl allows developers to test APIs directly from the command line, facilitating direct request and response interactions, which streamlines testing and boosts productivity through quick iterations.
Can Curl handle file downloads and uploads?
Yes, Curl can be used to download files from specified URLs and manage uploads, making it an essential tool for automating data workflows.
What features does Curl offer for file management?
Curl allows users to preserve original file titles or modify them during downloads, and it supports the --retry option for automatic attempts of failed requests, enhancing its robustness.
How does Curl manage redirects during data retrieval?
Curl manages redirects seamlessly using the -L flag, ensuring uninterrupted data retrieval.
Can you provide an example of a Curl command?
A typical Curl command to save response data to a file is curl https://api.example.com/data --output response.json, which captures data from API responses directly into a file.




